Core Measures & Registries
Clinical Data Abstraction Outsourcing
ADN’s expert and trusted hospital Core Measures & Registry Clinical Data Abstraction Outsourcing Service reduces the burden on your facility so you can focus on proactive quality management.

HOW IT WORKS
We will work with your team to seamlessly integrate into your current system and data abstraction process.
Our Chart Abstraction Outsourcing Service can help your hospital or organization meet the data collection and reporting requirements of The Joint Commission (TJC), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and Get With The Guidelines (GWTG) and more.
With our clinical data abstraction services, your team can:
Save Budget Dollars by Outsourcing
Maintaining a data collection process in-house is often much more costly than outsourcing.
Eliminate Turnover Challenges
Recruiting, hiring, and training is a substantial time-drain and diversion of focus for both the department manager and the team.
Refocus Scarce Clinical Personnel
Use your data for performance improvement work rather than waste expertise on routine data entry.
case studies

How one healthcare system Smartsourced its Data Abstraction burden to save money and strengthen focus on their mission
case studies
How a leading Pennsylvania hospital outsourced data abstraction and got a better core measures app, both for less than their previous product-only contract
Reduce Costs
Take advantage of per-chart pricing to reduce costs, reallocate abstraction staff to frontline positions or other roles, then outsource those positions to shave budget dollars. Bundle with our Core Measures application to save even more.
Avoid Costs
Insourcing carries costs beyond salaries. Data shows the true cost per employee that includes benefits/taxes is 125% – 140% of the salary, not to mention soft/unknown costs and the manager’s time cost.
Shift from Generalists to Experts
Insourced teams typically rely on one or a few abstraction generalists who may also wear other hats. ADN’s team includes experts in many registries and measures who also stay updated on ever-evolving specifications.
Reduce Financial Risk
Insourced teams typically rely on one or a few abstraction generalists who may also wear other hats. ADN’s team includes experts in many registries and measures who also stay updated on ever-evolving specifications.Allowing a team of experts to manage your abstraction provides better protection from payment reduction from abstraction errors made due to diverted focus or lack of sufficiently consistent training. Let us be an extension of your team and business.
Improve Business Focus
Focus your time and energy on the key goal leadership expects of quality directors and managers: Building a High-Reliability Organization. Offload the time-consuming management of abstraction to expertly trained, skilled specialists.
Refocus Resources
Abstraction is complex and time consuming for your already stretched resources. Reallocate existing and scarce staff who are needed either to help in frontline care positions or to implement and monitor improvement tactics and initiatives.
Increase Agility & Flexibility
Reducing the need to manage abstraction allows your department to more quickly implement improvement strategies or to more quickly adapt to risks and threats. Gain confidence, reduce overhead, keep headcount low, and leave data collection headaches to the experts.
Prepare for Future Challenges
Prepare for future financial and operational threats like the current pandemic, as well as other challenges, by freeing up your time and budget to better plan and weather future events.
Our success
Clinical Data Abstraction Smartsourcing By
The Numbers
Saving
Improvement
Accuracy

Time spent on performance improvement BEFORE Smartsourcing
Before smartsourcing with us, most of our clients dedicated around 70 to 80% of their time to data collection, leaving only 20 to 30% for performance improvement efforts.
Clinical workflow is no walk in the park. Hospital staff juggle a plethora of responsibilities and often lack the time and resources needed to accomplish everything on their to-do list. After smartsourcing, they’re able to focus their scarce clinical resources on more impactful, core-competency work of improving patient care.
Conduct more performance improvement AFTER Smartsourcing Data Abstraction to ADN
- Improving their treatment of and physician engagement around Sepsis;
- Improving their Stroke Program;
- Managing and Increasing Efficiencies for Patient Services: Appointments and discharges, follow-up care, and emergency department service;
- Improving overall patient care.
Industry-leading accuracy
Nothing is more important to us than accuracy and stability. ADN is dedicated to the ongoing education of our abstractors, and we uphold a rigorous Inter-Rater Reliability policy — maintaining an overall accuracy score of 98% or higher. That’s over the entire service line — all measures, all abstractors, all clients.
Improvement
Accuracy
the adn difference
Why partner with us?
You’ll be receiving the top medical record abstraction talent in the industry with high accuracy. You can easily get a person on the phone whenever you have a question. And you can trust that we can accommodate changes in your workload.
We are prepared and equipped for rapid ramp-up, meaning onboarding can happen swiftly.
Our team can also scale up or down based on your needs. We’ve had clients who’ve started out with a PRN assignment of just a few measures or data abstraction registries and later moved to full data abstraction outsourcing — handing off all of their medical chart abstraction burdens. We’ve also had multiple clients who initially outsourced for just one facility but then came back and added multiple hospitals to our assignment. ADN can accommodate these shifts with ease.
For more than a decade, we’ve offered Core Measures and Registry Data Abstraction. Despite the growth of these services, we’ve still retained our inaugural clients through our unmatched expertise, client service, flexibility, and customer support.
We will work directly with your facility to provide a solution that fits your needs – whether it’s full or partial outsourcing or even PRN for an abstraction backlog. Plus, our experienced abstraction specialists will work with any EHR and vendor tool you use.
We understand that sharing control of the abstraction process can be hard at first. Some facilities start by outsourcing just a few measures or a single registry to get a feel for the process before committing to a more extensive engagement. Then, most, if not all, go on to outsource more of their abstraction burden after the experience of working hand-in-hand with a trusted and conscientious partner.
Accuracy is not an accident; it’s a byproduct. We’ve spent more than a decade refining and strengthening our industry-leading data abstraction process, resulting in our 98.4%+ accuracy rate. And one of the core tenets of first-rate clinical data abstraction is a strong inter-rater reliability program. ADN consistently employs the best abstractors in the industry. Of the thousands of abstractor applicants we get per year, less than 1.5% pass our rigorous testing and vetting process. Top talent coupled with ADN’s philosophy of continuous improvement is what makes our IRR process second to none.
Nothing is more important to our team than giving you the peace of mind that your data abstraction is completed accurately and on time. Our team maintains industry-leading accuracy of 98.4% across all measures and registries, all abstractors, all clients.
Many of our clients expressed that previous data abstraction companies and vendors they worked with wouldn’t provide timely answers; they felt like just a number in a large company’s group of customers.
Our team responds to your requests within 24 hours. It’s not a policy — it’s a team mindset. We track our response time and take it seriously. It’s one thing to say clients come first; it’s another thing to act like it.
When it comes to selecting an outsourcing partner, the most important aspect that can vary dramatically between companies is the pedigree of its qualified clinical data registry staff. All of our data experts have worked in healthcare settings as nurses and quality staff or managers. They have an average of 23 years of experience in health care. Most have Bachelor’s degrees while others have Master’s degrees in areas including Nursing and Public Health.
All of our abstractors are cross-trained on multiple measure sets and registries, so they can easily transition between assignments as client needs evolve. Having been a Core Measures vendor for over 20 years and implementing a highly successful data abstraction service for more than 13, our team’s knowledge of Core Measures and registries is immense.
Our team is familiar with and comfortable working in all major EHRs and data collection tools. At any given time, our team is using 15 to 20 different EHRs and vendor tools.
Many on our team have also either already attained or are on a pathway to achieving the credential of Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality through the National Association for Healthcare Quality. ADN team members are active within NAHQ including having served on its board of directors.
ADN champions a company culture that inspires excellence and perpetuates long-term staffing and client engagement. We embrace a coaching/mentoring approach to employee relations and management. Our leadership understands that in order to sustain a team that invests fully in the success of its clients, ADN must first invest in the success of each of its team members. As a result, we have long-term clients because we have happy, long-term employees.
Staff vacancies can be a real source of anxiety and frustration, but a partnership with ADN will provide an essential safety net for your department. Planned or unplanned departures, illness, vacation, temporary, or extended leave are no longer a challenge by extending your department with our team, which can easily handle the additional workload.
the process
How does the process of outsourcing clinical data abstraction work?
-
Introduction &
needs assessment -
Onboarding:
Step 1 -
Onboarding:
Step 2 -
Onboarding:
Step 3 -
Onboarding:
Step 4 -
start work & absorb
caseloads

Partnership Fit & Pain Points Discussion
To learn more about your needs and how our team can support your goals. In this phase we’ll accomplish the following milestones:
- Discovery call to meet and learn about your specific needs
- Volumes survey completion to assess the scope of abstraction work
- Pricing proposal delivery & review
- Contract development, legal review and signing

Logistics Meeting
To establish a strong plan that will ensure a smooth transition. Make introductions, gather details around your current quality program and our new assignment, as well as discuss preferred processes, workflows, and deadlines.

Assign Experts & Establish Access
To assign a dedicated account lead and team of abstractors who are carefully matched to your facility’s populations and systems. Then, to ensure access to your EHR and vendor systems for assigned abstractors as ADN works within your existing process. We’re experienced with all EHRs and vendor tools.

Orient to Documentation Tendencies
To thoroughly review relevant clinical documentation practices so our abstractors can learn about tendencies that are particular to your facility and EHR.
Demonstrate Accuracy & Establish Trust
To perform inter-rater reliability on a sample of cases to ensure our abstraction team has mastered your documentation practices and is performing at the accuracy rate ADN requires.

Within 30 Days of Access
Our team will lift the data collection burden off your shoulders and start abstracting while you begin focusing more personnel and resources than ever on performance improvement.
the adn difference
FAQs about Clinical Data Abstraction Outsourcing
Our team makes weekly progress on all populations, with a typical turnaround time of 30 days after our team receives your patient lists. While a 30-day turnaround is most typical, we work closely with our clients to align timelines with established processes. ADN has the resources and personnel to ramp up very fast and meet your data abstraction needs.
Our clinical data abstractor training is designed to be comprehensive and rigorous, ensuring the highest standards of accuracy and efficiency. Our training program includes:
- Testing and Vetting: We start with a stringent testing and vetting process for all potential hires. This ensures that only those with a solid background and experience in clinical data abstraction join our team.
- Initial Training: Experienced abstractors undergo initial training to familiarize them with our specific processes, client needs, and registry requirements. This includes detailed instruction on our data abstraction techniques, coding standards, and client-specific guidelines to ensure seamless integration into our workflows.
- Ongoing Education: To keep up with evolving standards and guidelines, our abstractors participate in continuous education. This includes regular updates on changes to guidelines, new best practices, and advancements in data abstraction technology.
- Quality Assurance: We implement strict quality assurance measures, including regular inter-rater reliability (IRR) assessments, to ensure our abstractors maintain the highest levels of accuracy and consistency in their work.
- Hands-On Experience: Our training includes practical, hands-on experience with real-world data abstraction scenarios. This helps our abstractors develop the skills and confidence needed to handle the complexities of clinical data abstraction efficiently.
- Support and Feedback: Our abstractors receive ongoing support and feedback from our team of experienced account leads. This includes one-on-one mentoring, regular performance reviews, and access to a wealth of resources to help them continuously improve their skills.
By investing in such rigorous training, we ensure that our abstractors are well-equipped to deliver precise and reliable data abstraction services, ultimately helping our clients achieve their quality improvement goals.
The majority of our agreements for data abstraction services are annual contracts. Although, we are flexible and can craft engagements tailored to fit your needs, whether that be to address a one-time backlog or a full outsourcing partnership.
IRR (Inter-Rater Reliability) is performed throughout the clinical data lifecycle on a sample of cases for each and every measure and registry that we are abstracting for your organization. First, IRR is performed at the beginning of the engagement, prior to the start of the data abstraction assignment, to ensure assigned abstractors have a strong understanding of your documentation tendencies. After that, our team performs routine IRR to ensure accuracy remains at our high standards. Additionally, there are a number of events that can trigger ADN to perform IRR outside the regular cadence. These include but are not limited to specification changes to measures or registries, expansions of our SOW, or assignment of a new abstractor to your account.
Your dedicated ADN account lead will provide feedback throughout the life of your engagement with ADN and will ensure that all of the team members assigned to your account function as an extension of your quality department. ADN can provide additional consulting services that extend beyond chart abstraction, including follow-up, special reports or analytics, and compensation can be easily handled with an hourly management fee.
During the initial logistics meeting, we will work closely with your team will to establish exactly how communication around fallouts should be handled. Your team will also continue to monitor OFIs by running and reviewing the reports available in your data collection tool. It’s also common for ADN to utilize a spreadsheet housed in a shared drive to track OFIs within specific measure sets and registries. Additionally, your ADN account lead can attend regular meetings where improvement opportunities are discussed, in which case we would use the hourly management fee to handle compensation.
One of the reasons we’re able to maintain our position as the industry leader in accuracy is our stringent vetting and testing process for new hires. Of the thousands of applicants we get in a year, only about 1.5% pass the proprietary tests we’ve developed to accurately assess an abstractor’s knowledge and skills. Of the abstractors that have made the cut, our experts have an average of 23 years of experience working in healthcare settings as nurses, doctors, and Quality managers or staff. Many also have their CPHQ credential or are working to attain it.
Healthcare analytics Tools & resources
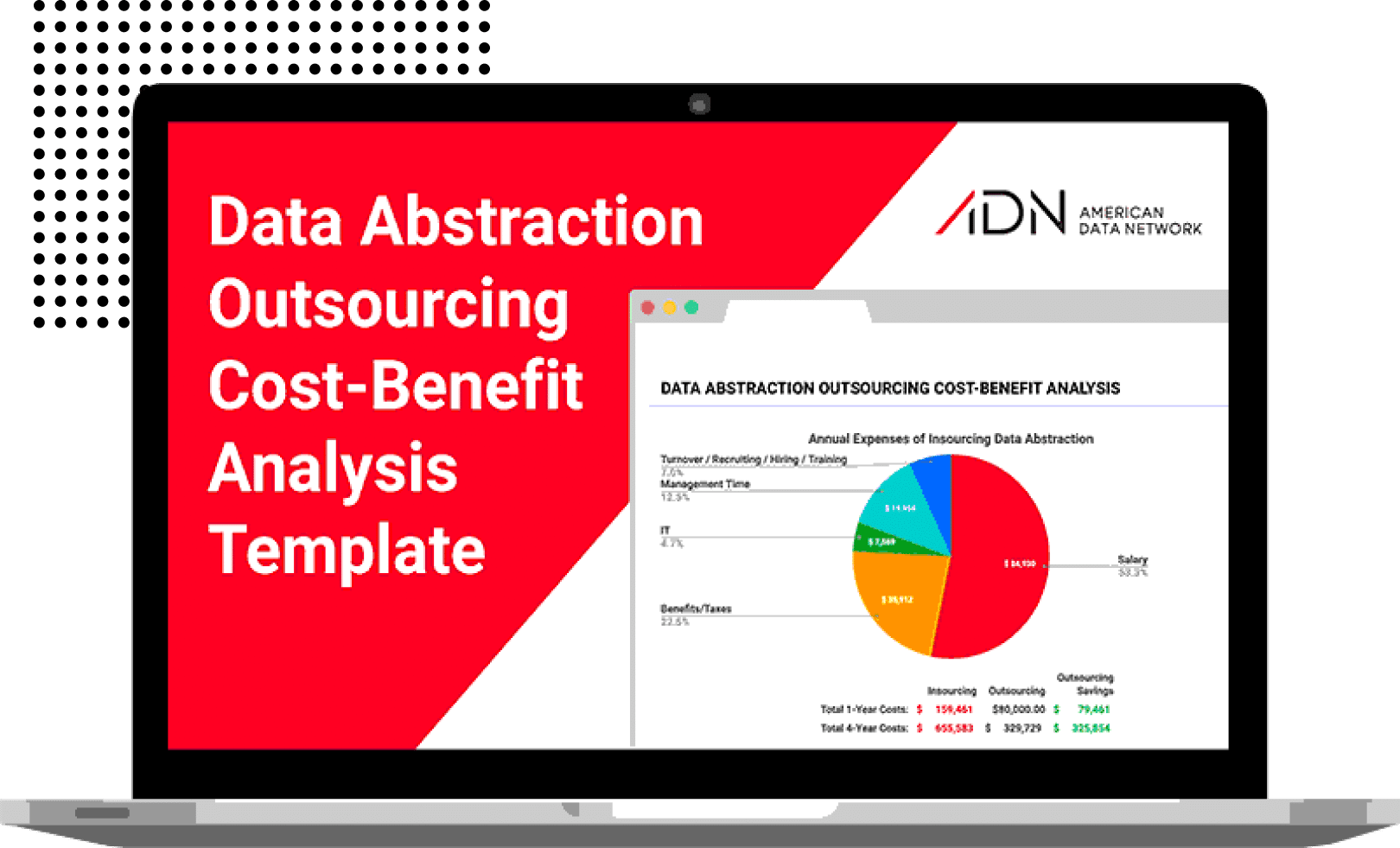
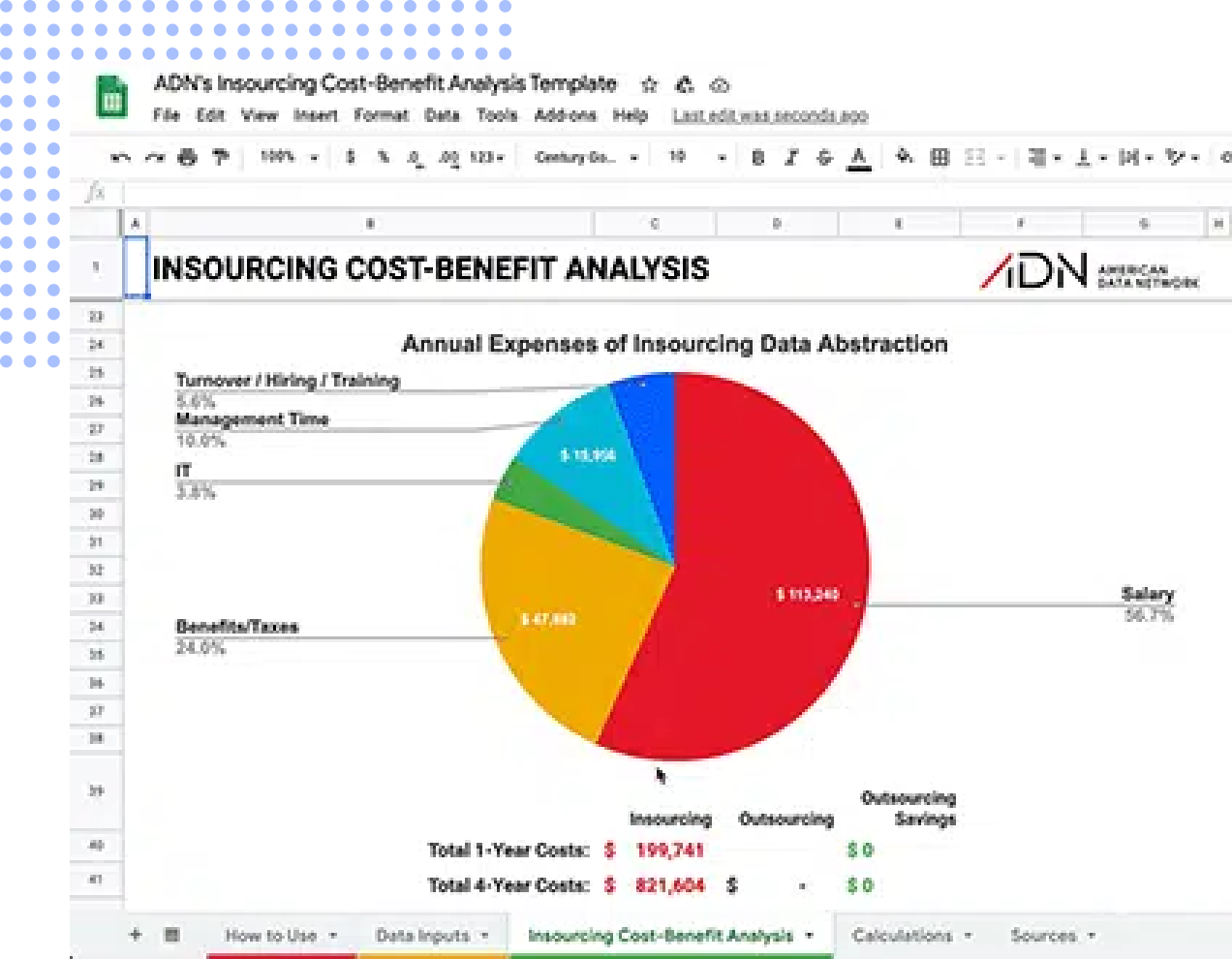
Free Outsourcing Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
As many facilities are evaluating how to utilize scarce clinical resources, reallocating data abstraction staff to quality improvement and outsourcing abstraction positions can shave critical budget dollars. American Data Network’s “Outsourcing Cost-Benefit Analysis Template” can help you determine the true cost of your in-house data abstraction process. In under three minutes, this tool will show you and your leadership team total savings and where they will come from using real data and expert resources.
we have it covered
Clinical Data Registries We Abstract
-
Clinical Data Registries
we abstract -
State-specific Programs
we abstract -
Hospital Core Measures
we abstract
The CathPCI Registry® assesses the characteristics, treatments and outcomes of cardiac disease patients who receive diagnostic catheterization and/or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures. This powerful tool captures the data that measure adherence to ACC/AHA clinical practice guideline recommendations, procedure performance standards and appropriate use criteria for coronary revascularization.
For over a decade, the Chest Pain – MI (formerly ACTION) Registry® has been the single, most trusted source for outcomes-based, continuous quality improvement focusing exclusively on high-risk STEMI/NSTEMI patients. The registry collects and delivers detailed, in-hospital clinical, process-of-care and outcomes data for patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). See Top 15 Reasons to Participate in the Chest Pain – MI (formerly ACTION) Registry.
This allows for complex decision making to maximize patient care while lowering risk and health care costs. It also helps hospitals apply the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) clinical guideline recommendations in their facilities and provides invaluable tools to measure care and achieve quality improvement goals.
The EP Device Implant RegistryTM is your most trusted source of evidence-based data collection and reporting for ICD/CRT-D procedures. Participating in the EP Device Implant Registry is still your most reliable way to track ongoing compliance with the updated CMS National Coverage Determination (NCD). The EP Device Implant Registry plays an important role in determining the association between evidence-based treatment strategies and clinical outcomes.
With the IMPACT Registry®, gain access to a multi-institutional data set to support the development of evidence-based guidelines and review performance benchmarks to guide quality improvement for pediatric and adult congenital heart disease (CHD) patients who undergo diagnostic and interventional catheterizations
The PVI RegistryTM assesses the prevalence, demographics, management and outcomes of patients undergoing lower extremity peripheral arterial catheter-based interventions and includes carotid artery stenting (CAS) and carotid endarterectomy (CEA). The PVI Registry provides data collection and equips clinicians with decision-making data whether care is provided in a hospital cath lab, interventional radiology department, or an outpatient vascular center.
The STS/ACC TVT RegistryTM , created by a collaboration between the Society for Thoracic Surgeons and the ACC, monitors patient safety and real-world outcomes related to transcatheter valve replacement and repair procedures – emerging treatments for valve disease patients. Employing state-of-the-art heart valve technology, transcatheter heart valve procedures provide new treatment options for patients who are not eligible for conventional heart valve replacement or repair surgery.
The STS National Database was established in 1989 as an initiative for quality improvement and patient safety among cardiothoracic surgeons. As of January 1, 2018, the STS National Database has four components, each focusing on a different area of cardiothoracic surgery—Adult Cardiac Surgery, General Thoracic Surgery, and Congenital Heart Surgery, as well as mechanical circulatory support via the Intermacs Database. The Database has grown exponentially over the years, both in terms of participation and stature
The STS National Database was established in 1989 as an initiative for quality improvement and patient safety among cardiothoracic surgeons. As of January 1, 2018, the STS National Database has four components, each focusing on a different area of cardiothoracic surgery—Adult Cardiac Surgery, General Thoracic Surgery, and Congenital Heart Surgery, as well as mechanical circulatory support via the Intermacs Database. The Database has grown exponentially over the years, both in terms of participation and stature.
SVS VQI’s 14 registries contain demographic, clinical, procedural and outcomes data from more than a million vascular procedures performed across the United States, as well as Canada and Singapore. Each record includes information from the patient’s initial hospitalization and at one-year follow-up.
- The wealth of data allows centers and providers to compare their performance to regional and national benchmarks.
- Each center and provider receive biannual dashboards and regular performance reports, so they can use their data to support quality improvement initiatives.
- Biannual regional meetings allow physicians, nurses, data managers, quality officers, and others to meet, share information and ideas, and learn from each other in a positive and supportive environment.
Where SVS VQI data are used to:
- Significantly improve the delivery of vascular care at a local and national level, reducing complications and expenses.
- Stratify risk, analyze outcomes, develop quality improvement, define best clinical practices, assess comparative effectiveness research and improve resource utilization.
- Facilitate participation in clinical trials and other medical device evaluation efforts.
- Collaborate with multiple organizations, including the American College of Cardiology, Society of Interventional Radiology, governmental regulatory agencies, device manufacturers, and payers
- Help provide clinically detailed data for device performance, post-market surveillance, and label expansion
- Partner with vascular registries from Europe and Asia to form the International Consortium of Vascular Registries (ICVR) to bring a global perspective to improving vascular care and device evaluation.
Many hospitals have trouble tracking surgical complications and may lack the data necessary to analyze and take appropriate steps to fix problem areas. You can’t improve a hospital’s surgical quality if you can’t measure it; and for that you need robust, valid data. Yet 59 percent of surveyed sites were unaware of their hospital’s surgical complication rate before they joined the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program®
ACS NSQIP data enhances a hospital’s ability to zero in on preventable complications. Because it was developed by surgeons who understand the realities of the operating room, ACS NSQIP helps hundreds of hospitals across the country gauge the quality of their surgical programs with unrivaled precision and measurably improve surgical outcomes.
With more than 1,200 centers worldwide submitting data on VLBW and all NICU admissions, the reporting tools give centers the necessary data and benchmarks to make meaningful local improvement.
Teams in the improvement programs (NICQ and iNICQ) participate in VON Day Audits, point-prevalence quality audits that include unit-level and patient-level measures for benchmarking and to inform their improvement projects. Teams in NICQ also work with homeroom faculty to identify VON data items for special reports.
Get With The Guidelines®-Stroke is an in-hospital program for improving stroke care by promoting consistent adherence to the latest scientific treatment guidelines. Since its initiation in 2003, 1,656 hospitals have entered more than two million patient records into the Get With The Guidelines-Stroke database. Numerous published studies demonstrate the program’s success in achieving measurable patient outcome improvements.
Certified Comprehensive Stroke Centers are required to meet the performance measurement requirements for Primary Stroke Centers, including the collection of data for the eight stroke core measures and submission of monthly data points every quarter through the Certification Measure Information Process (CMIP).
Get With The Guidelines®-Heart Failure is an in-hospital program for improving care by promoting consistent adherence to the latest scientific treatment guidelines. Numerous published studies demonstrate the program’s success in achieving significant patient outcome improvements. Among the proven results are reductions in 30-day readmissions, a measure now used by CMS in determining CMS reimbursement rates.
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) affects between 2.7 and 6.1 million Americans, often leading to heart-related complications as well as increasing the risk for stroke fivefold. Get With The Guidelines®-AFIB is the newest addition to the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s collaborative performance improvement programs. The program is designed to assist hospital care teams in consistently providing the latest evidence-based treatment for their AFib patients. At the same time, it offers a means of monitoring the quality of AFib care in U.S. hospitals and building a database for continued research and further quality improvement.
GWTG-CAD is available as a tool to track AMI process data
GWTG-R facilitates the efficient capture, analysis and reporting of data that empowers and supports the implementation of current guidelines, creation and dissemination of new knowledge, and development of next generation, evidence-based practice in resuscitation science. Its mission is to save more lives by preventing in-hospital cardiac arrest and optimizing outcomes through benchmarking, quality improvement, knowledge translation, and research.
Trauma registries used document acute care delivered to patients hospitalized with injuries. They provide data to identify and drive process improvement activities that will reduce morbidity and mortality from traumatic events.
CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network is the nation’s most widely used healthcare-associated infection tracking system. NHSN provides facilities, states, regions, and the nation with data needed to identify problem areas, measure progress of prevention efforts, and ultimately eliminate healthcare-associated infections.
In addition, NHSN allows healthcare facilities to track blood safety errors and important healthcare process measures such as healthcare personnel influenza vaccine status and infection control adherence rates.
The Pediatric Cardiac Critical Care Consortium (PC⁴) aims to improve the quality of care to patients with critical pediatric and congenital cardiovascular disease in North America and abroad. Formed in 2009 with National Institutes of Health funding, PC⁴ is a unique collaborative of leaders in pediatric cardiac critical care, cardiac surgery, and cardiology representing a diverse group of centers caring for these vulnerable patients. The core pillars of collaborative quality improvement serve as the foundation for PC⁴: purposeful collection of specific clinical data on outcomes and practice; timely performance feedback to clinicians, and continuous improvement based on empirical analysis and collaborative learning.
We created the Medicare Beneficiary Quality Improvement Program (MBQIP) to improve the quality of care patients receive in Critical Access Hospitals (CAHs) (PDF – 2 MB).
MBQIP focuses these efforts in the 45 states that participate in the Medicare Rural Hospital Flexibility (Flex) Program. Through Flex, MBQIP works with 1,360 rural Critical Access Hospitals (CAHs) to use quality measure data for quality improvement activities.
MBQIP supports CAHs in reporting on quality measures. Most quality measures are collected through the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) quality reporting programs.
These measures help CAHs understand health care processes, outcomes, patient perceptions of care, and organizational structure to guide decisions about improvements to health care services.
Quality improvement efforts focus on strategies for hospitals serving smaller patient groups those found in urban areas.
The California CABG Outcomes Reporting Program (CCORP) is currently collecting and reporting CABG operative mortality data for all California hospitals and surgeons that perform the CABG procedure.
The data collection and reporting standards required of prehospital providers to support the quality improvement process for the Cardiac Care System.
The Inpatient Quality Incentive (IQI) program provides millions of dollars in performance bonus payments to hospitals that improve care for clinical priorities of the Arkansas Medicaid program. The IQI program requires hospitals to meet specific goals for a number of quality measures – certain aspects of care proven to improve outcomes for patients. Hospitals also must pass validation to receive payment or recognition.
The Riverside County EMS STEMI System encompasses a network of prehospital 9-1-1 EMS providers and hospitals receiving STEMI patients. This program focuses on patients who suffered confirmed STEMI heart attacks in Riverside County, with data being added quarterly and available for comparison on a continuous basis. Cases are those patients transported via 9-1-1 ambulances to Riverside County STEMI receiving centers.
The goals of the program include: 1) Reducing E2B times (monitoring EMS to balloon times and reducing to under 90 minutes 90% of the time), 2) increasing pre-activation of cath lab teams (increasing EMS notification to 80% of the time), and 3) providing 100% feedback from confirmed and suspected EMS transported STEMI cases to providers (including discharge diagnosis, hospital disposition and discharge summary).
Certified Comprehensive Stroke Centers are required to meet the performance measurement requirements for Primary Stroke Centers, including the collection of data for the eight stroke core measures and submission of monthly data points every quarter through the Certification Measure Information Process (CMIP).
The Clinical Outcomes Assessment Program (COAP) is a Washington State initiative designed to produce clinical information needed to improve quality of care and meet the growing demand for accountability in the health care industry.
COAP’s physician-led Management Committee, in partnership with State officials and key stakeholders, has created this program as a model of collaboration in which Washington State’s cardiac community can work together toward a common goal — improving patient care and health outcomes. COAP’s timely reporting mechanism provides hospitals with clinical feedback on a quarterly basis.
Inpatient Measures
Decrease decision to admit time and time patients spend in ED
Increase flu immunization rates in high risk patients
Monitor increase in elective deliveries and decrease non-emergent C-Section deliveries
Measures timely management of sepsis and septic shock to decrease organ failure, mortality, LOS and cost
Monitor interventions and appropriate discharge instructions for stroke patients
Decrease VTEs through monitoring, prophylaxis, and utilization of best practices
Admission screenings, events and transitions to next level of care
Adherence to standardized performance measures addressing alcohol screening and cessation counseling
Adherence to standardized performance measures addressing tobacco screening and cessation counseling
Measures the percentage of patients discharged with an antipsychotic prescription for which a structured metabolic screening for: (1) BMI; (2) blood pressure; (3) glucose or HbA1c; and (4) lipid panel was completed in the past year.
The movement of a patient from one setting of care (hospital, ambulatory primary care practice, ambulatory specialty care practice, long-term care, home health, rehabilitation facility) to another.
Outpatient Measures
The Social Drivers of Health (SDOH) measure by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) assesses the impact of non-medical factors on health outcomes. The SDOH measure assesses patients 18 years and older for food insecurity, housing instability, transportation needs, utility difficulties, and interpersonal safety. While 20% of health outcomes are linked to medical care, 80% are influenced by these factors, which disproportionately impact communities of color and have worsened due to COVID-19.
Monitors timeliness of evaluation and treatment of patients arriving in ED
Head CT or MRI Scan Results for Acute Ischemic Stroke or Hemorrhagic Stroke Patients who Received Head CT or MRI Scan Interpretation Within 45 minutes of ED Arrival
Improvement in Patient’s Visual Function within 90 Days Following Cataract Surgery
Description: Median time from hospital arrival in the emergency department to transfer of a hemorrhagic stroke patient or an ischemic stroke patient to another hospital.
Appropriate follow-up interval for patients with and without history of polyps
The Emergency Department Transfer Communication measure provides hospitals with a means of assessing how well key patient information is communicated from an emergency department to any healthcare facility. The measure applies to patients with a wide range of medical conditions (e.g., acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, pneumonia, respiratory compromise and trauma) and is relevant for both internal quality improvement purposes as well as external reporting to consumers and purchasers.
Don’t see the registry or custom abstraction project you need help with? No problem.
Our team does custom registry and state-specific projects. Just reach out to us and we can discuss your needs.
With the demand for public reporting, we turned to American Data Network to assist with the burden of data collection. They had the experience and know-how to take on all of our Core Measures responsibilities.
Outsourcing our Core Measures abstractions has freed up our staff, allowing them to concentrate on focused clinical areas. We are now able to spend more time on using the data to improve the quality of patient care at Mt. Sinai.

Mount Sinai Medical Center
Get In Touch With Us
Contact Sales
Contact Support

Are you an existing customer looking for help with a particular issue?
Or give us a call at (501) 225-5533, we love helping customers.
Resources
Our Products
Our Services
Get In Touch
10809 Executive Center Drive
Searcy Building, Suite 300
Little Rock, AR 72211
(501) 225-5533
(501) 222-1083 Fax